Developmental and acquired brain injury have opposite effects on finger coordination in children
Aug 23, 2023·,,,,, ·
0 min read
·
0 min read
Aviva Mimouni-Bloch
Sharon Shaklai
Moran Levin
Moria Ingber
Tanya Karolitsky
Sigal Grunbaum
Jason Friedman
Abstract
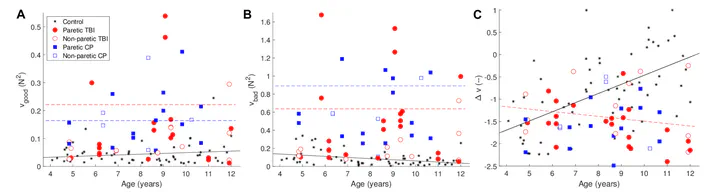
The ability to coordinate finger forces to dexterously perform tasks develops in children as they grow older. Following brain injury, either developmental (as in cerebral palsy–CP) or acquired (as in traumatic brain injury—TBI), this developmental trajectory will likely be impaired. In this study, we compared finger coordination in a group of children aged 4–12 with CP and TBI to a group of typically developing children using an isometric pressing task. As expected, deficits were observed in functional tests (Jebsen Taylor test of hand function, Box and Block test) for both groups, and children in both groups performed the pressing task less well than the control group. However, differing results were observed between the CP and TBI groups when using the uncontrolled manifold hypothesis to look at the synergy index. This index measures the relative amount of “good” (does not affect the outcome measure) and “bad” (does affect the outcome measure) variability, where in this case the outcome measure is the total force produced by the fingers. While children with CP were more variable in their performance, their synergy index was not significantly different from typically developing children, suggesting the development of compensatory strategies. In contrast, the children following TBI showed performance that got worse as a function of age (i.e., the older children with TBI performed worse than the younger children with TBI). These differences between the groups may be a result of different areas of brain injury typically observed in CP and TBI, and the different amount of time that has passed since the injury.
Type
Publication
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience